Why I Changed From NPM/Yarn to PNPM and Why You Should, Too!
I recently came across a useful tool called PNPM and wasn’t sure if it was worth my time until I saw a benchmark image comparing NPM, YARN, and PNPM. I immediately noticed that PNPM is 3x faster than the others in terms of installing dependencies, so I said I must give it a try.

Package managers are software tools that help programmers and developers install, update and uninstall code, libraries, or other software packages.
Any user can add or remove a package from this common pool. Packages are usually retrieved from remote servers, but can also be installed locally.
What is a Package Manager?
A package manager is a piece of software that handles computer software packages’ installation, upgrading, and removal.
A package manager stores packages in a central location on the hard disk or network drive. It allows multiple users to share a single copy of the package.
Package managers, like npm install and yarn add, are often CLI-based. Usually, JavaScript applications have many dependencies, and those dependencies are managed by a package manager.
Node uses NPM by default. However, NPM does not have some advanced features that are ideal for more advanced applications, or it is slow when installing packages or solving package dependencies.
Yarn and PNPM, which are community-made package managers, came into existence to solve the above problem.
In the past few years, the yarn has become slower, but today it’s probably the most popular option.

NPM ⚡YARN ⚡PNPM -
NPM is a package manager for JavaScript that was originally developed by the Node.js project. It enables developers to share code more easily across different projects and use other people’s code in their projects.
Yarn is a package manager for JavaScript and it was developed by Facebook. It is fast, reliable, and secure.
PNPM is a new package manager for JavaScript that was built on top of npm to simplify the installation process of packages in node applications. PNPM is an alternative to NPM. It follows the same principles as NPM but it has some additional features that make it more powerful than its predecessor.
Performance / Disk -
NPM: It is a bit slower when compared to Yarn and PNPM.
YARN: Yarn uses the same flattened node_modules directory but it is comparable to NPM in regards to speed and installs packages parallelly.
PNPM: PNPM is 3 times faster and more efficient than NPM. With both cold and hot cache, PNPM is faster than Yarn.
👉 Pnpm simply links files from the global store, while yarn copies files from its cache.
Package versions are never saved more than once on a disk.
🙌 The algorithm of pnpm does not use a flattened dependency tree, which makes it easier to implement, and maintain, and requires less computation. 😀

PNPM grouped all dependencies by symlink but retained all the dependencies.
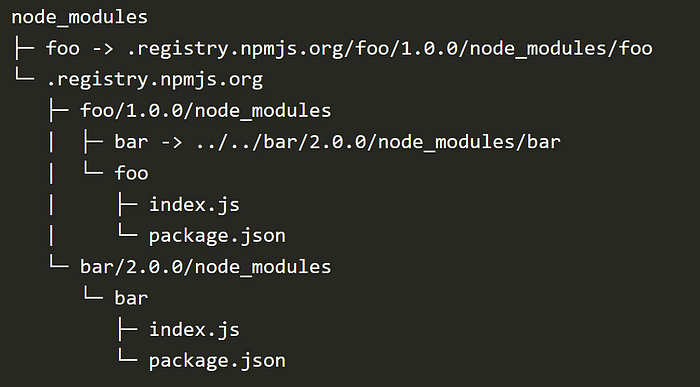
PNPM can also save space compared to the other two package managers.
Monorepo support -
A Monorepository consists of multiple isolated code repositories all in one repository in order to avoid managing multiple repositories.
NPM: The NPM package manager offers monorepo support with a variety of CLI commands to manage multiple packages. However, unlike other package managers, it does not support advanced filtering or multiple workspaces.
YARN: It also offers monorepo support as the feature workspaces. Using Lerna, a third-party application, before the workspace feature was available, was the only way to use the package manager in a multi-package project.
PNPM: NPM’s doppelgangers problem can only be solved with PNPM. Monorepos are sometimes plagued with doppelgangers, so PNPM has an advantage in this regard.
Security -
NPM: There have been some security vulnerabilities that have directly affected many projects due to the way npm handles bad packages.
YARN: Checksums stored in yarn.lock have been used by Yarn Classic and Yarn Berry ever since. Yarn also prevents installing malicious packages;
👉 If a mismatch is detected, the installation will be aborted.
PNPM: Similar to Yarn, PNPM also uses checksums and in addition to the use of checksums, pnpm also verifies the integrity of its code before executing it.
Installation Workflows -
A package manager has to be installed locally and CI/CD first.
NPM: It is one of the world’s largest package registry, which should be installed with Node.js. It uses the package.json and package.lock.json files.
npm install "package_name"
YARN: To come over from the problems of NPM, YARN was developed. It provided many new features that were later incorporated with npm such as lockfile with versions, caching and so on.
npm install -g yarn
PNPM: You can easily install PNPM with npm package.
npm install -g pnpm
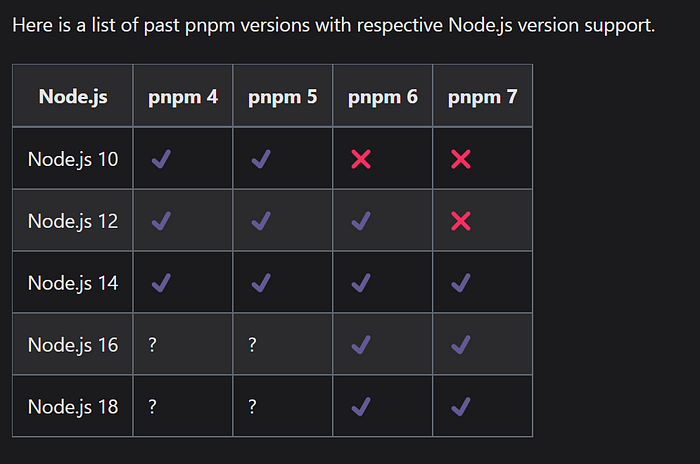
Compatibility
Troubleshooting -
If pnpm is broken and you cannot fix it by reinstalling, you might need to remove it manually from the PATH.
Feature Comparison -


Thanks 🙏 for reading !!
Please 🤝 follow me for more stories !!
